Anti-Microbial Resistance in India: Causes, Consequences & Prevention - IAS EXPRESS

There are a number of diseases that occur due to microbes (microorganisms) like bacteria, virus, and parasites. Antibiotics fight against these microbes and they are widely used in the treatment and for preventing infections. However, the problem arises when people consume these antibiotics frequently. This creates antibiotic resistance where the drug does not benefit human health, but of the microbes as they are used to the drug. By the year 2050, antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is estimated to account for around 10 million deaths each year around the world, of which 2 million are expected to occur in India alone. Around 30% of neonatal sepsis deaths in India are associated with AMR. Therefore India, a pharma super-power, should fix this grave threat of antimicrobial resistance.
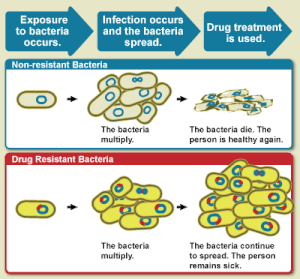
Antimicrobial resistance - Wikipedia
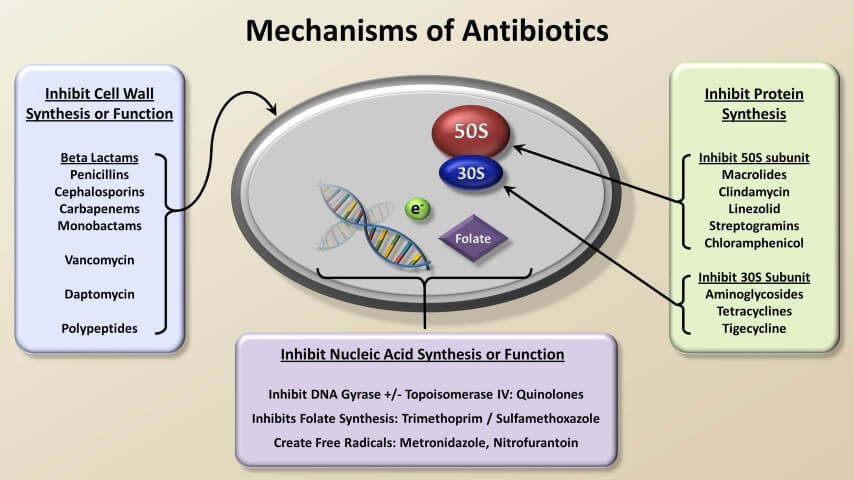
Antimicrobial Resistance, Causative Factors, Measures Taken - PMF IAS

Menace of antimicrobial resistance in LMICs: Current surveillance

Climate Change and Sustainable Food Security - ePrints@NIAS
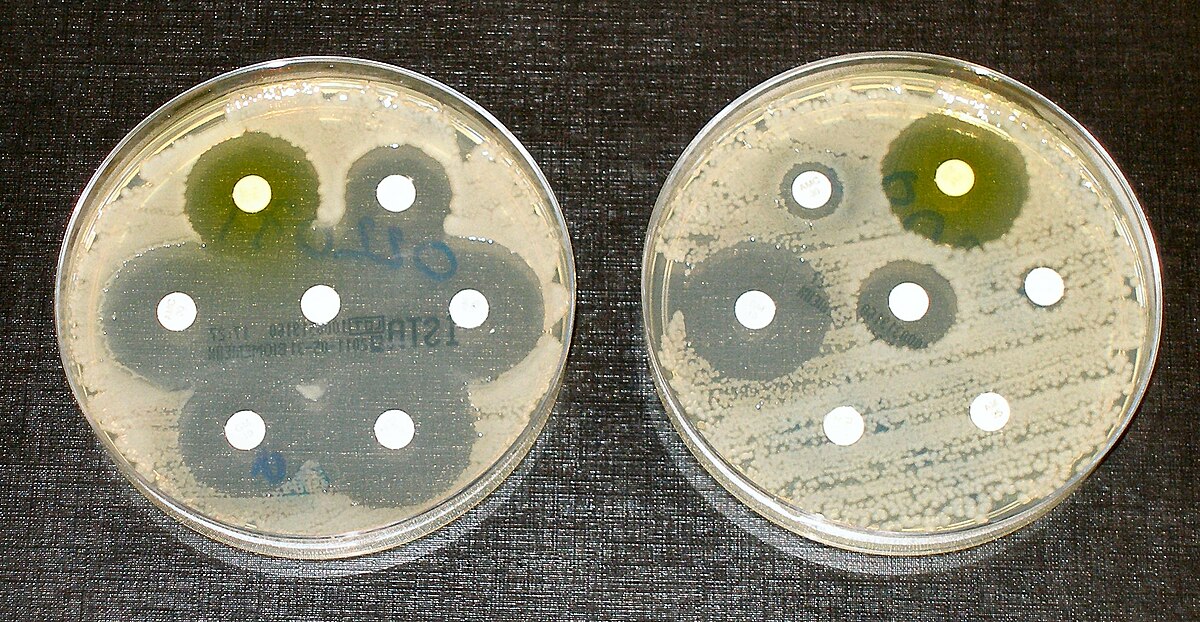
Antimicrobial resistance - Wikipedia

Antimicrobial Resistance

A systematic review and meta-analysis on prevalence and

Antimicrobial Resistance: The Silent Threat - Current Affairs

GLOBAL RESEARCH ON ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE (GRAM) REPORT - IAS Gyan

Antibiotics Resistance - Civilsdaily

PDF) Antibiotics and Bacterial Resistance in the 21st Century

Are rising air pollution and PM 2.5 directly linked to antibiotic

Antimicrobial resistance - Wikipedia
One Health - Current Affairs