PDF] Computed Tomography Measurement of Rib Cage Morphometry in Emphysema

This study demonstrates that simple CT measurements can predict rib cage Morphometric variability and also highlight relationships between rib cage morphometry and emphysema. Background Factors determining the shape of the human rib cage are not completely understood. We aimed to quantify the contribution of anthropometric and COPD-related changes to rib cage variability in adult cigarette smokers. Methods Rib cage diameters and areas (calculated from the inner surface of the rib cage) in 816 smokers with or without COPD, were evaluated at three anatomical levels using computed tomography (CT). CTs were analyzed with software, which allows quantification of total emphysema (emphysema%). The relationship between rib cage measurements and anthropometric factors, lung function indices, and %emphysema were tested using linear regression models. Results A model that included gender, age, BMI, emphysema%, forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1)%, and forced vital capacity (FVC)% fit best with the rib cage measurements (R2 = 64% for the rib cage area variation at the lower anatomical level). Gender had the biggest impact on rib cage diameter and area (105.3 cm2; 95% CI: 111.7 to 98.8 for male lower area). Emphysema% was responsible for an increase in size of upper and middle CT areas (up to 5.4 cm2; 95% CI: 3.0 to 7.8 for an emphysema increase of 5%). Lower rib cage areas decreased as FVC% decreased (5.1 cm2; 95% CI: 2.5 to 7.6 for 10 percentage points of FVC variation). Conclusions This study demonstrates that simple CT measurements can predict rib cage morphometric variability and also highlight relationships between rib cage morphometry and emphysema.

Correlation between quantitative multi-detector computed tomography lung analysis and pulmonary function tests in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients, Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine
Bronchiectasis Imaging: Practice Essentials, Radiography, Computed Tomography

Quantifying lung and diaphragm morphology using radiographs in normative pediatric subjects, and predicting CT‐derived lung volume - Orbach - 2021 - Pediatric Pulmonology - Wiley Online Library

image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1mdmcqcases-23

PDF) Computed Tomography Measurement of Rib Cage Morphometry in Emphysema
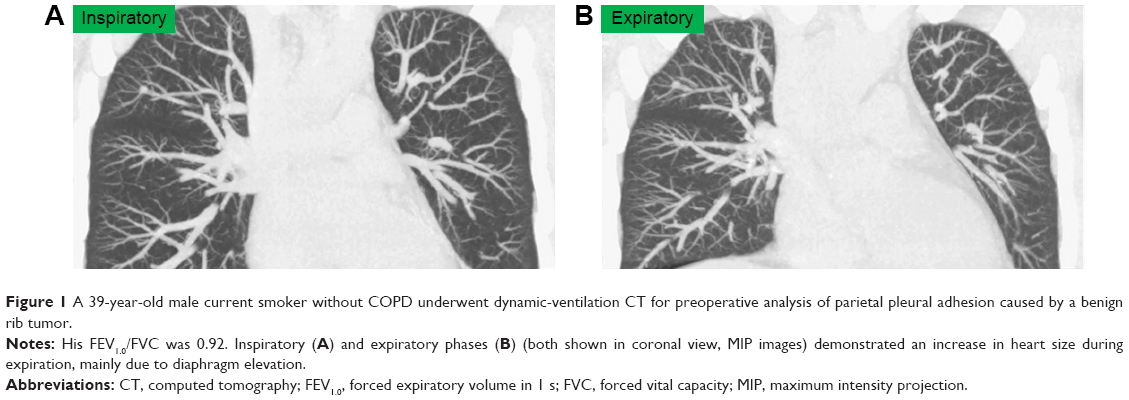
Hyperinflated lungs compress the heart during expiration in COPD patie

Textbook of Radiology For CT and MRI Technicians With, PDF, X Ray

JCM, Free Full-Text
PDF) Computed Tomography Measurement of Rib Cage Morphometry in Emphysema

3D segmentation and visualization of lung and its structures using CT images of the thorax
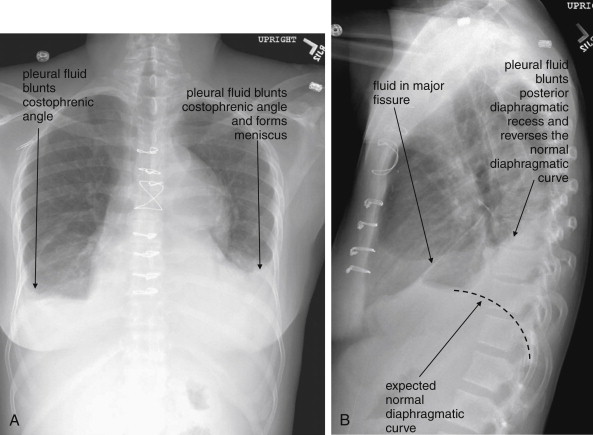
Imaging the Chest: The Chest Radiograph

Aging Airways: between Normal and Disease. A Multidimensional Diagnostic Approach by Combining Clinical, Functional, and Imaging Data
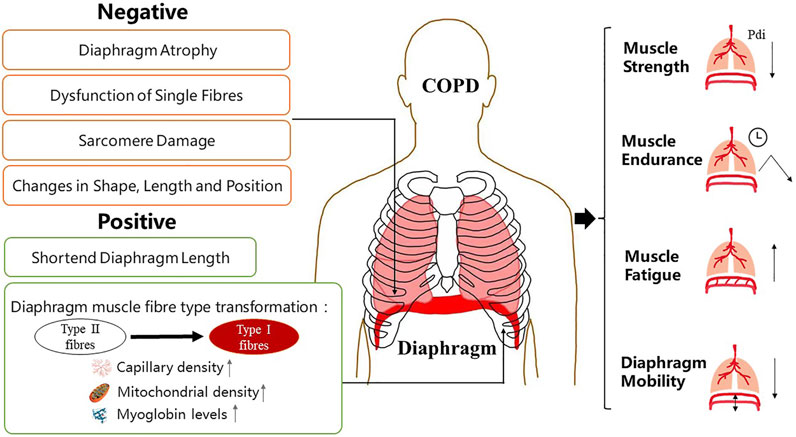
Frontiers Diaphragm Dysfunction and Rehabilitation Strategy in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease