Shared and modality-specific brain regions that mediate auditory and visual word comprehension
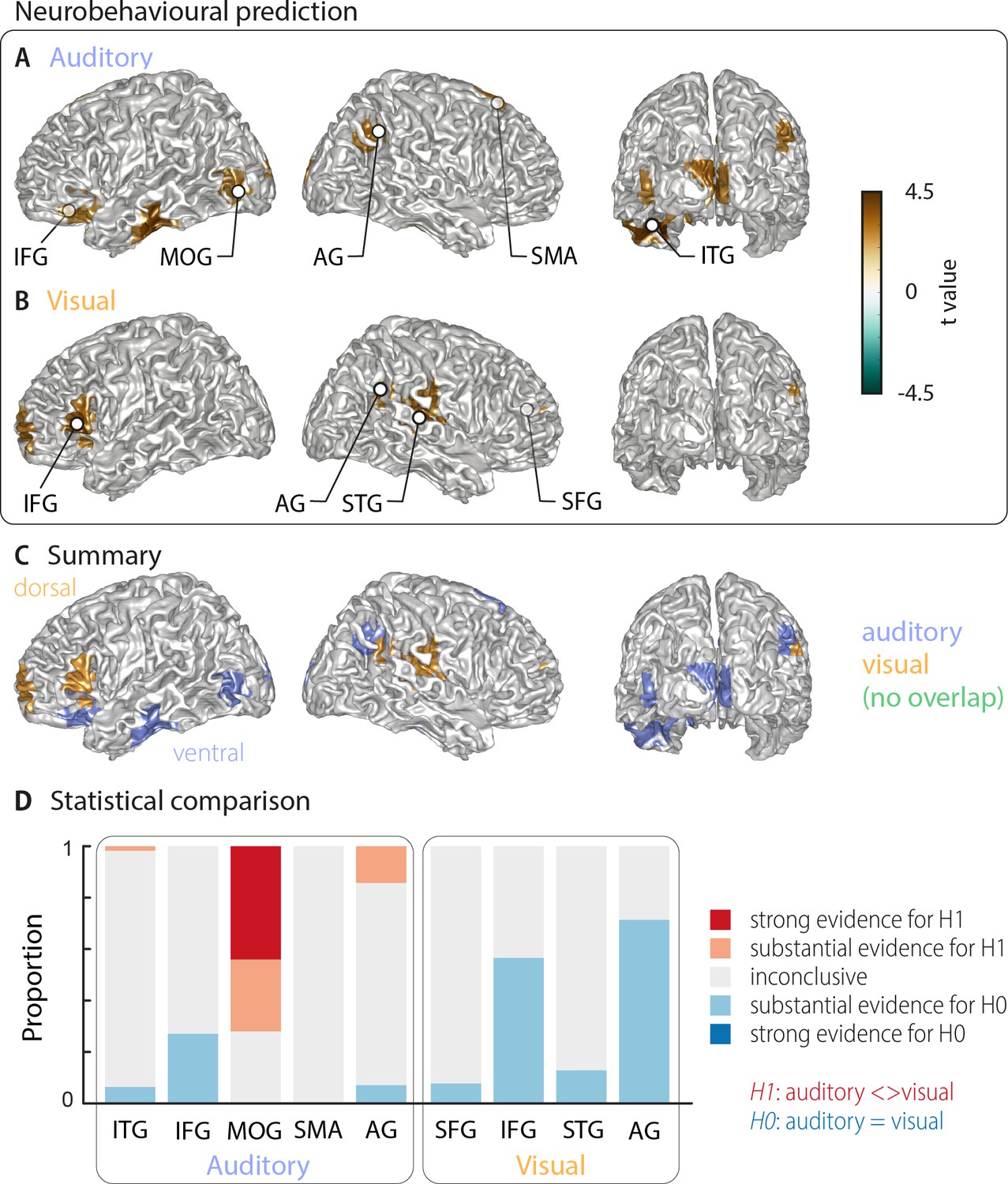
The comprehension of acoustic and visual speech depends on modality-specific pathways in the brain, which explains why auditory speech abilities and lip reading are not associated in typical adults.

i-EEG results in patient 1. (A) Spectrograms of /ba/, /da/, and

PDF) MEG Activity in Visual and Auditory Cortices Represents

Contralateral attentional modulation of Steady State Responses. In

Contralateral cortical tracking of underlying quasi-rhythmic

Christoph KAYSER, Bielefeld University, Bielefeld

Artificial intelligence based multimodal language decoding from

Spatial dynamics of behaviour--relevant brain activity. A

Regions of interests (i.e., masks) in the superior temporal lobes

Decoding in all patients. Time course of the decoding accuracy

AV integration common to all stimulus classes. A , Activations

Lip movements enhance speech representations and effective

Temproal response function (TRF) timecourse and topography. A

Areas activated for the conjunction non-lexical lip-reading and