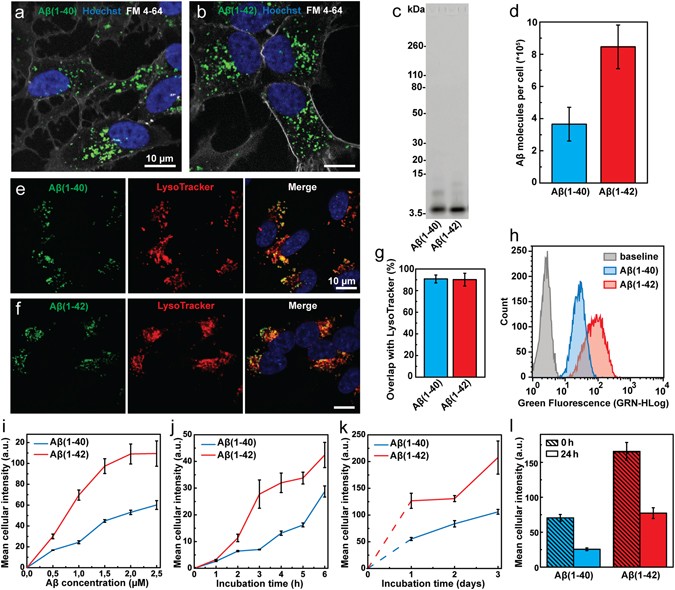
Endocytic uptake of monomeric amyloid-β peptides is clathrin- and dynamin-independent and results in selective accumulation of Aβ(1–42) compared to Aβ(1–40)

Towards the integrative theory of Alzheimer's disease: linking molecular mechanisms of neurotoxicity, beta-amyloid biomarkers, and the diagnosis

Cell surface proteoglycan-mediated uptake and accumulation of the Alzheimer's disease peptide Aβ(1–42) - ScienceDirect

Evidence for aggregation-independent, PrPC-mediated Aβ cellular internalization. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Uptake of Aβ(1-40), Aβ(1-42) and Trf in SH-SY5Y cells under conditions
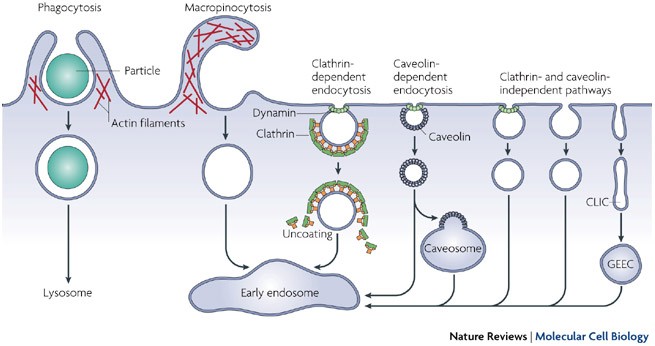
Pathways of clathrin-independent endocytosis

Amyloid-beta peptides 40 and 42 employ distinct molecular pathways for cell entry and intracellular transit at the BBB endothelium
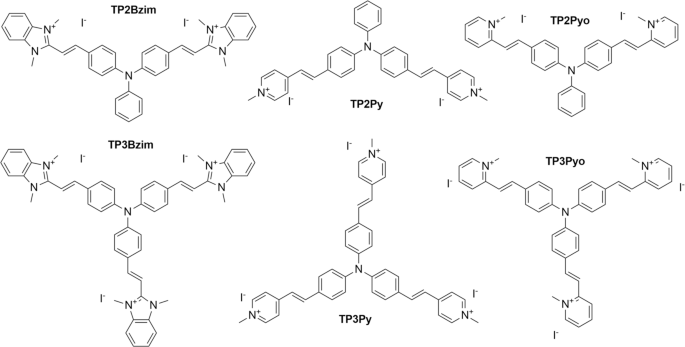
Interplay between Cellular Uptake, Intracellular Localization and the Cell Death Mechanism in Triphenylamine-Mediated Photoinduced Cell Death

Alzheimer's disease linked Aβ42 exerts product feedback inhibition on γ-secretase impairing downstream cell signaling

Designed Cell-Penetrating Peptide Inhibitors of Amyloid-beta Aggregation and Cytotoxicity - ScienceDirect

IJMS, Free Full-Text

Misfolded amyloid-β-42 impairs the endosomal–lysosomal pathway