Elucidation of the mechanism whereby prostanoid TP receptor stimulation enhances urinary bladder smooth muscle contractions induced by parasympathetic neurotransmitters – TOHO UNIVERSITY
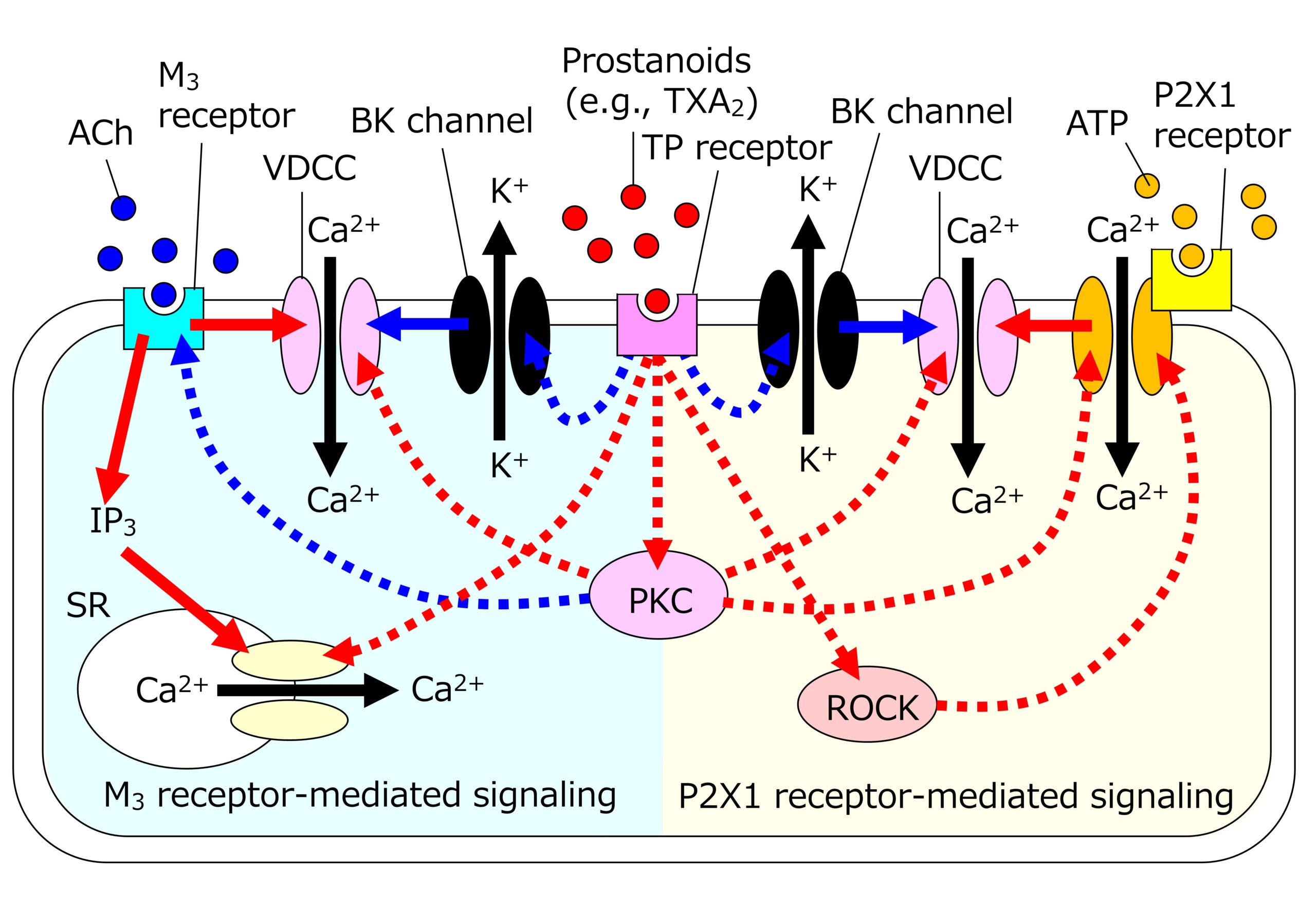

Prostanoid TP receptor stimulation enhances contractile activities in guinea pig urinary bladder smooth muscle through activation of Ca2+ entry channels: Potential targets in the treatment of urinary bladder contractile dysfunction - ScienceDirect

Prostanoid TP receptor stimulation enhances contractile activities in guinea pig urinary bladder smooth muscle through activation of Ca2+ entry channels: Potential targets in the treatment of urinary bladder contractile dysfunction - ScienceDirect

Pirt reduces bladder overactivity by inhibiting purinergic receptor P2X3

Prostanoid TP receptor stimulation enhances contractile activities in guinea pig urinary bladder smooth muscle through activation of Ca2+ entry channels: Potential targets in the treatment of urinary bladder contractile dysfunction - ScienceDirect

Functional rewiring of G protein-coupled receptor signaling in human labor - ScienceDirect
Pirt reduces bladder overactivity by inhibiting purinergic receptor P2X3

Overactive bladder syndrome, polyuria, and nocturia

Keisuke OBARA, Doctor of Pharmacy, Toho University, Tokyo, Toho-U, Department of Chemical Pharmacology

Mechanotransduction in the urothelium: ATP signalling and mechanoreceptors - ScienceDirect
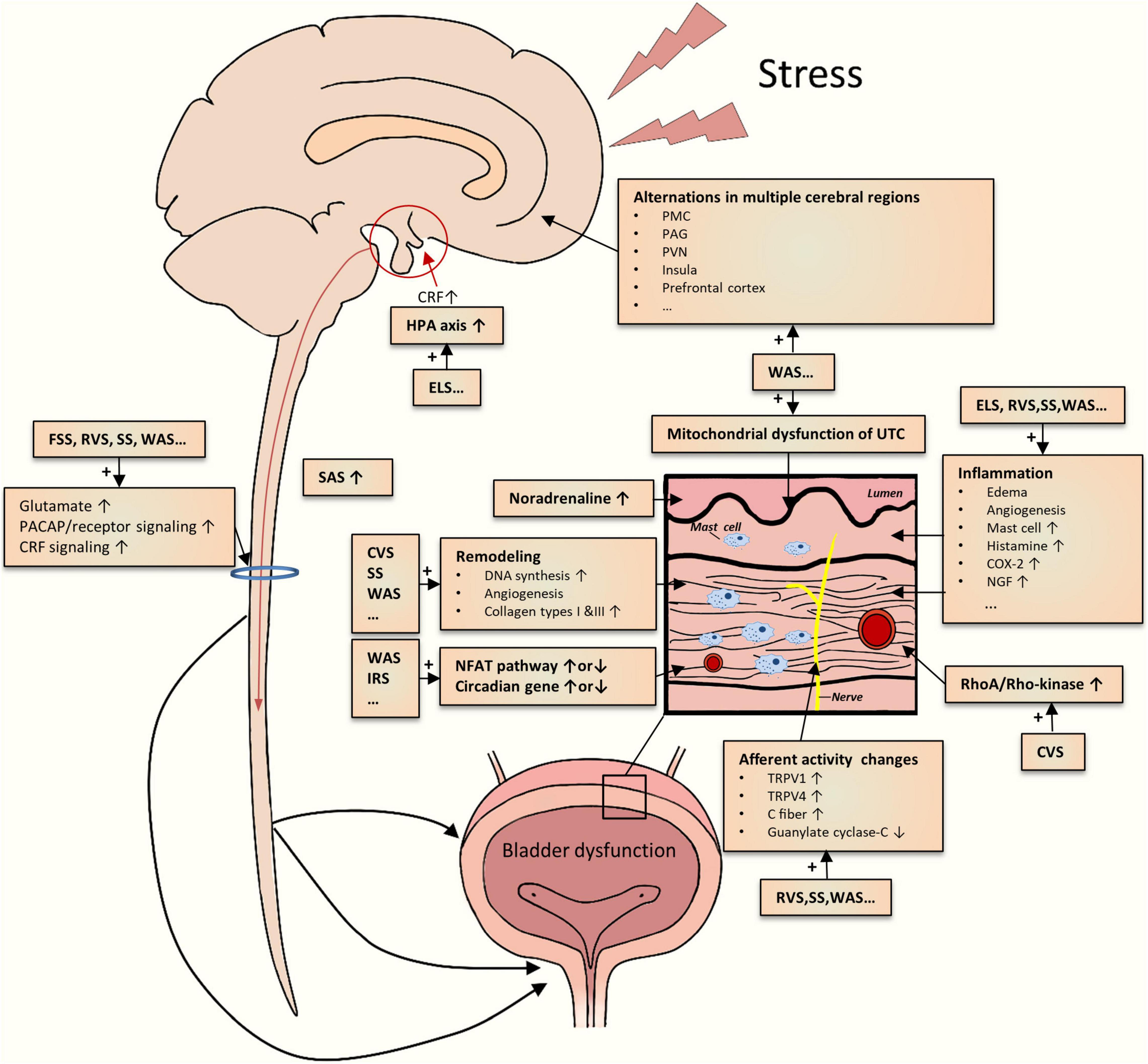
Novel Mechanisms Involved in Urinary Bladder Control: Advances in Neural, Humoral and Local Factors Underlying Function and Disease, Volume II
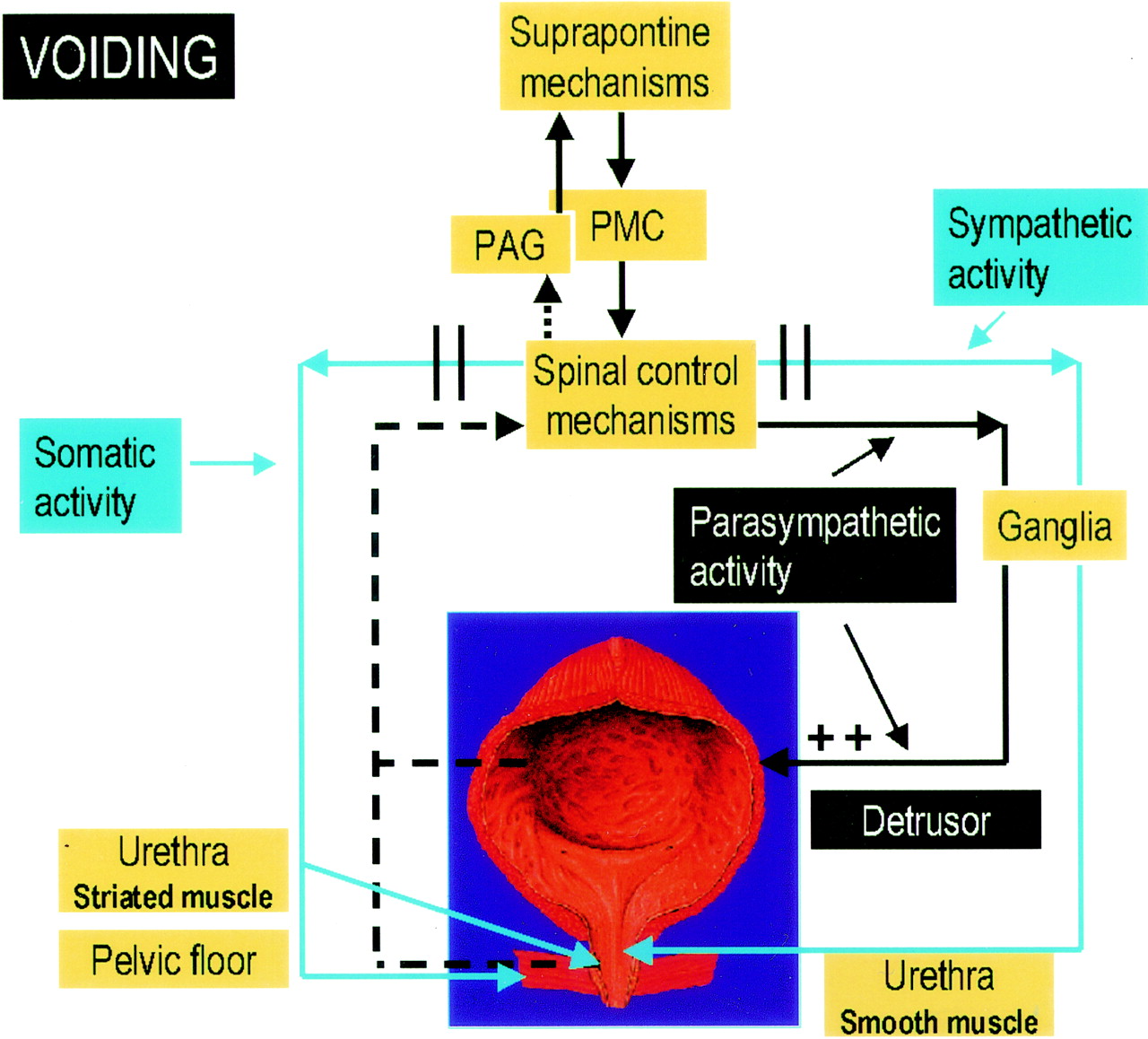
Pharmacology of the Lower Urinary Tract: Basis for Current and Future Treatments of Urinary Incontinence

Muscarinic receptor antagonists for overactive bladder - Abrams - 2007 - BJU International - Wiley Online Library