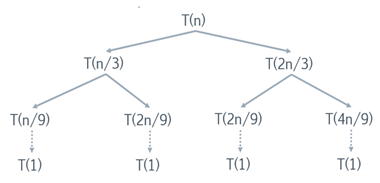
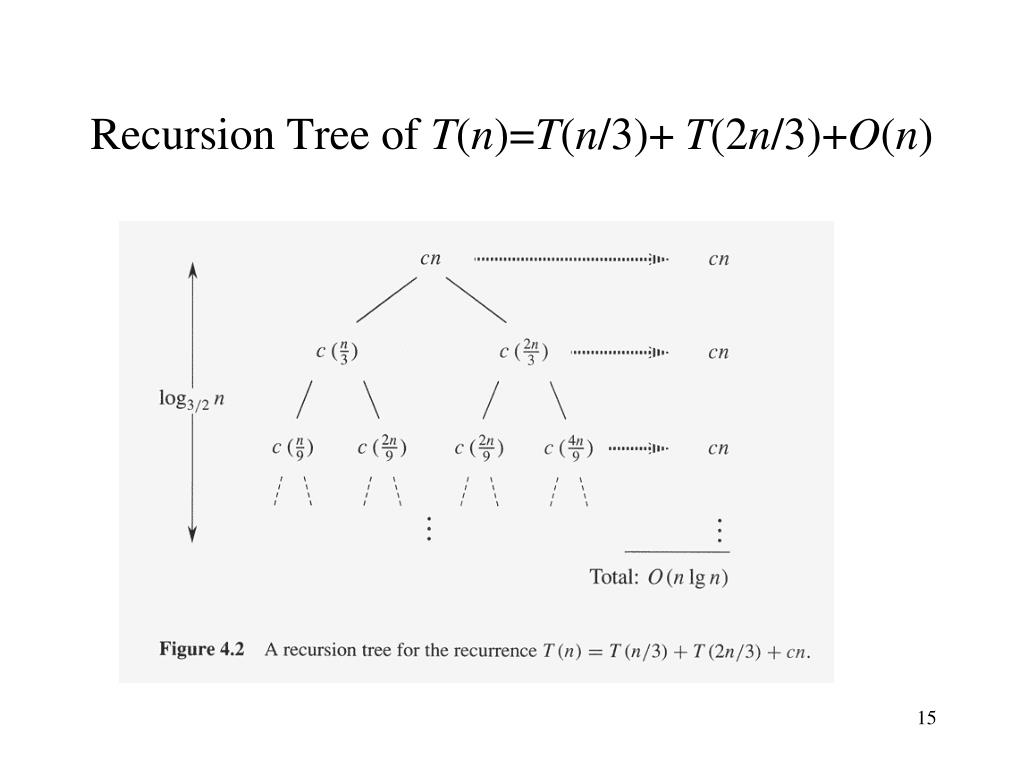
recursive algorithms - Recursion tree T(n) = T(n/3) + T(2n/3) + cn

I have a task: Explain that by using recursion tree that solution for: $T(n)=T(\frac n3)+T(\frac {2n}{3})+cn$ Where c is constance, is $\Omega(n\lg n)$ My solution: Recursion tree for $T(n)=T(\fra

How to solve time complexity Recurrence Relations using Recursion Tree method? - GeeksforGeeks

GATE 2021 ALGORITHMS RECURRENCE RELATION T(n)=T(n/2)

Algorithm] 1. Growth of functions and Solving recurrences, by jun94, jun-devpBlog

Recursion Tree Method to Solve Recurrences
Solved) - Solve the recurrence T(n)= 9T(n/3)+n.Solve the following - (1 Answer)
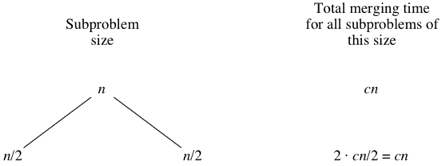
Analysis of merge sort (article)
PPT - Asymptotic Efficiency of Recurrences PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:1223916
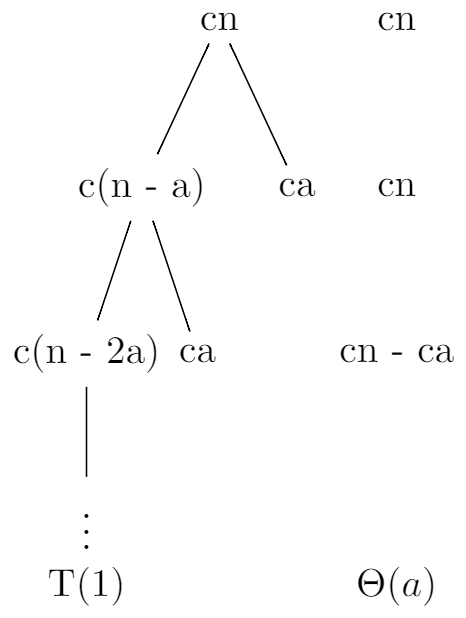
4.4 The recursion-tree method for solving recurrences - Introduction to Algorithms
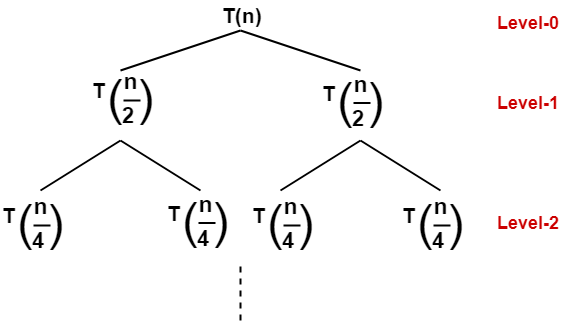
Recursion Tree, Solving Recurrence Relations

recursive algorithms - Recursion tree T(n) = T(n/3) + T(2n/3) + cn
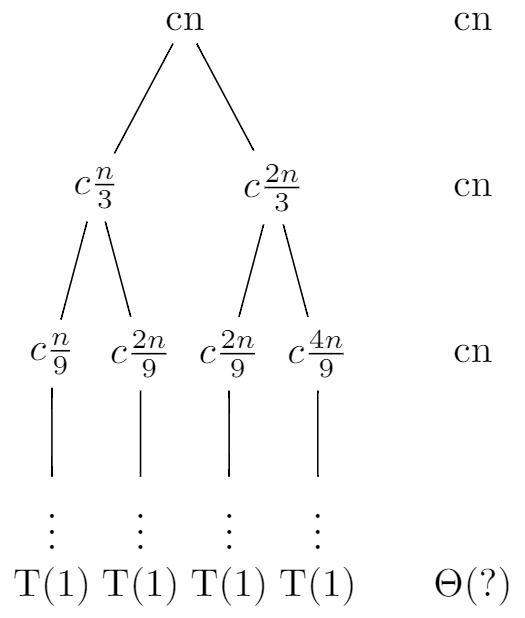
4.4 The recursion-tree method for solving recurrences - Introduction to Algorithms

SOLVED: 4.4-2 Use a recursion tree to determine a good asymptotic upper bound on the recurrence T(n) = T(n/2) + n². Use the substitution method to verify your answer. Constructing the tree

Analyzing Recursive Algorithms A recursive algorithm can often be described by a recurrence equation that describes the overall runtime on a problem of. - ppt download